Object Localization using ROS and AprilTag
This blog introduces how to employ AprilTag markers for localizing a target in 3-D space. This benefits tasks such as navigation, robot control, and augmentated reality. For preparations, you should have a camera ready.
Launching Camera
In our design, we connect a USB camera with the Raspberry Pi as the system’s visual input. We launch the camera video feed as ROS topics for further processing. Installation commands of the program are as follows:
cd workspace/src
git clone https://github.com/bosch-ros-pkg/usb_cam.git
cd ~/workspace
catkin_make
Note that errors may occur in the catkin_make process, which is probabily due to lack of relevant packages in the environment. Solutions are across the web.
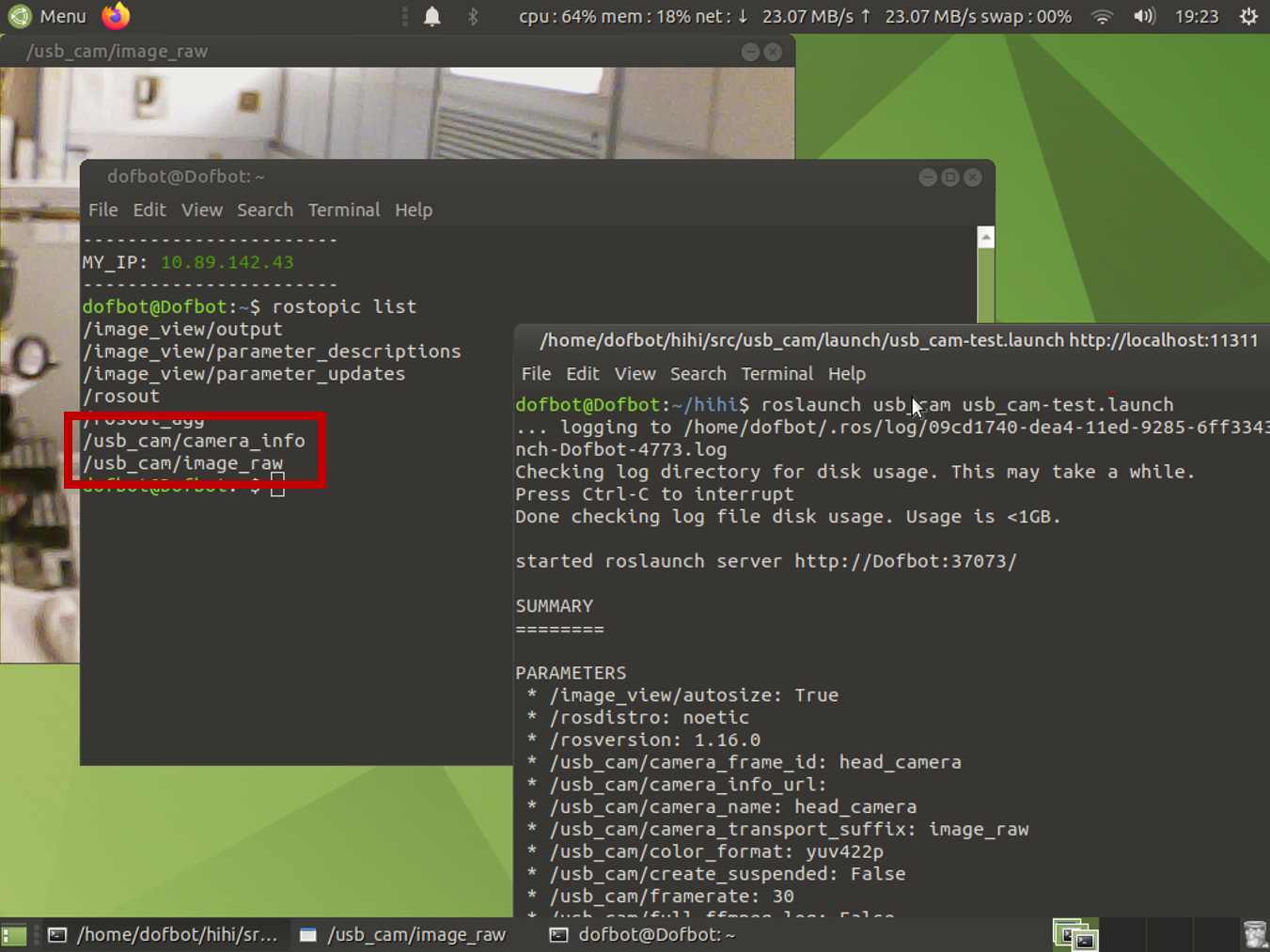
To launch the camera as ROS ropics, input the following command. As in the subsequent figure, the published topics surrounded by a red rectangle should appear.
source devel/setup.bash
roslaunch usb_cam usb_cam-test.launch
Camera Calibration
You may also encounter an error in the previous step, indicating that camera calibration has not been conducted. This procedure is needed to combat spatial distortion problems when measuring the size in world units. Using a standard figure such as a checkerboard, we can obtain the camera parameters including intrinsics, extrinsics, and distortion coefficients. This link explains the underlying mathematical principle, and this link introduces how to conduct camera calibration.
AprilTag Detection Algorithm
AprilTag is a visual fiducial system used in robotics and camera calibration. Targets are created from an ordinary printer, then the AprilTag detection software computes the precise 3D position, orientation, and identity of the tags relative to the camera. You can find some of the AprilTag (of tag family 36h11) at this link.
Installation
Official website, GitHub source code
Installation commands are as follows:
cd workspace/src
git clone https://github.com/AprilRobotics/apriltag_ros.git
cd ~/workspace
catkin_make
Config File
Go to apriltag_ros/launch/continuous_detection.launch. Alter the camera input configurations to subscribe to the ROS video feed. Note that the actual scenario may be slightly different, refer to this link for the technical details of the published topics.
<arg name="camera_name" default="usb_cam" />
<arg name="camera_frame" default="image_raw" />
<arg name="image_topic" default="image_rect" />
Go to apriltag_ros/config/tags.yaml. Add the target tags ID and measured size (in the unit of meters). For example:
standalong_tags:
[
{id: 0, size: 0.05}
{id: 1, size: 0.045}
]
Activate AprilTag Algorithm
First, launch the camera in ROS as in the previous section. Then enter the following commands one by one:
AprilTag Continuous Detection
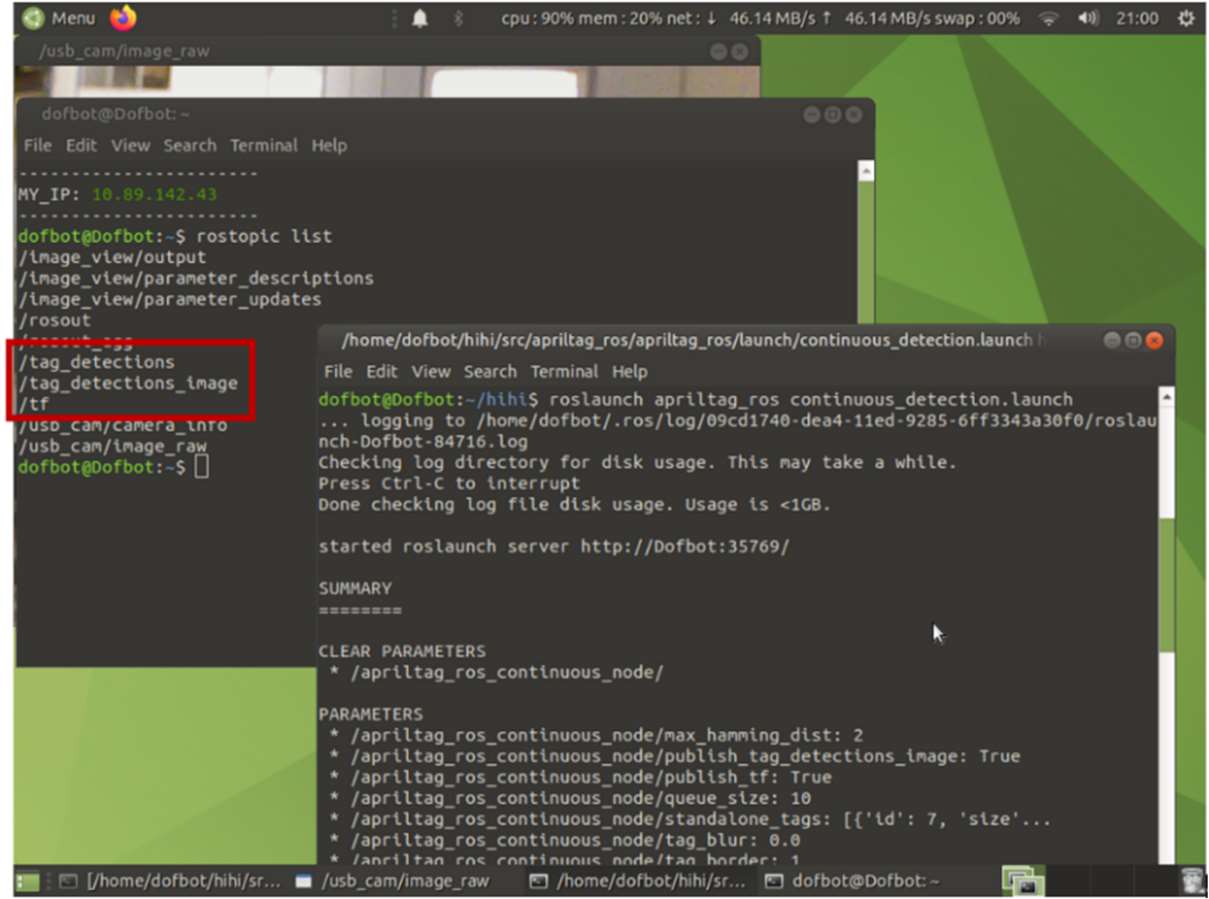
roslaunch apriltag_ros continuous_detection.launch
Upon successful launch, you should be able to examine the published topics surrounded in red rectangle as in the subsequent figure.
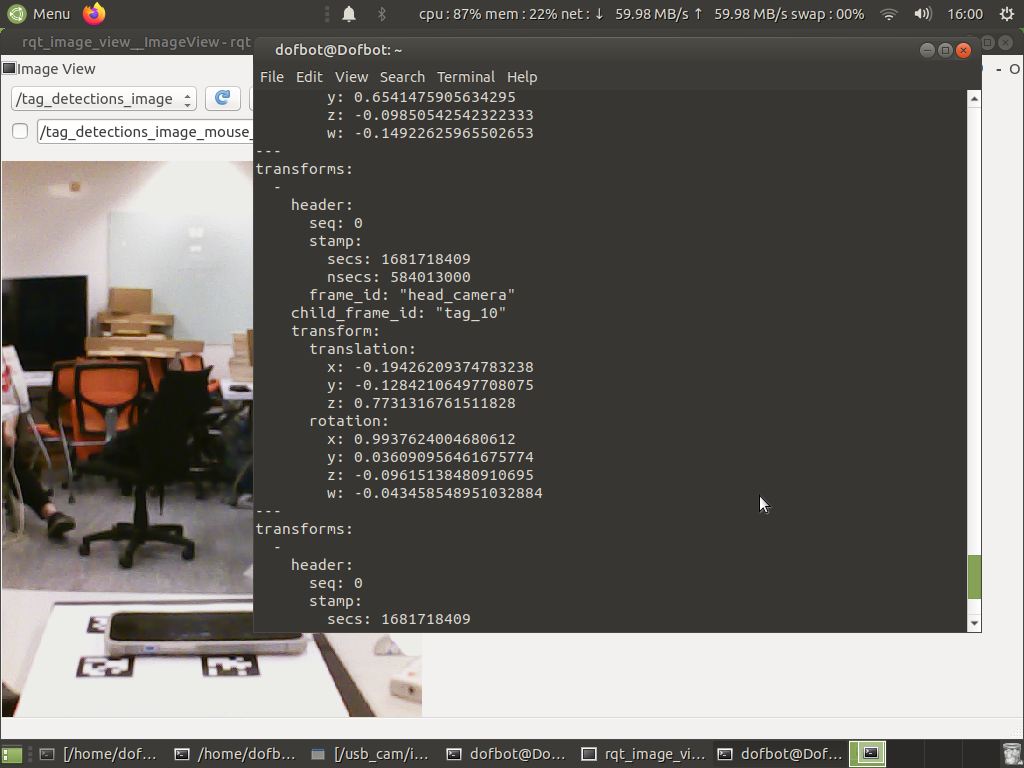
Detection Result
rqt_image_view
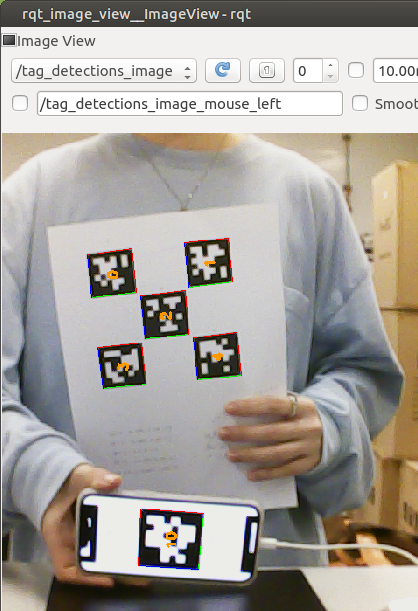
Localization Result
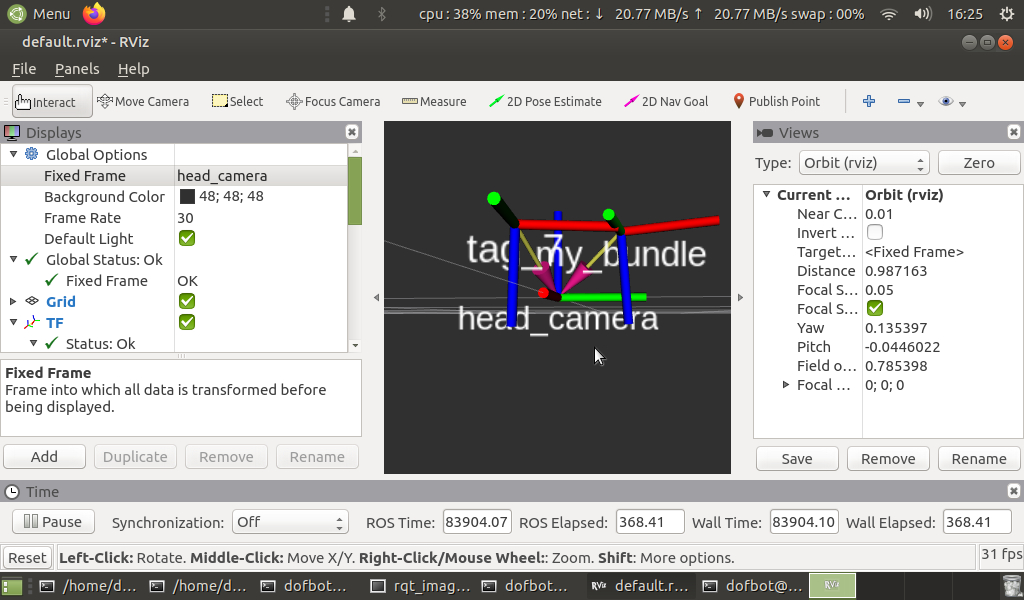
rosrun rviz rviz
This step activates the RViz visualization widget. You should be able to examine the localization result, which demonstrates the position of the target tags with respect to the head camera in the form of a transform tree.
rostopic echo /tag_detections
Next Steps
The AprilTag detection algorithm generates the position coordinates of the target tags with respect to the camera (or the other way round), including the position and orientation. Coordinates can be transformed to the world axes for more tasks.
